MS SQL Server¶
Table of contents
Introduction¶
Hasura allows connecting to a SQL Server database and build an GraphQL API based on the database schema.
Supported from
Hasura GraphQL engine v2.0.0-alpha.2 onwards
Supported SQL Server versions
Hasura GraphQL engine currently supports SQL Server 2016 and above.
Try it out¶
You can run Hasura with SQL Server using docker-compose and an existing SQL Server database
as follows:
Prerequisites¶
- Docker
- Docker Compose
- An existing SQL Server database
Step 1: Get the docker-compose file¶
Get the Hasura MS SQL Server docker compose file:
# in a new directory run
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hasura/graphql-engine/master/install-manifests/docker-compose-ms-sql-server/docker-compose.yaml
# or run
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hasura/graphql-engine/master/install-manifests/docker-compose-ms-sql-server/docker-compose.yaml -o docker-compose.yaml
Step 2: Run Hasura GraphQL engine¶
The following command will run Hasura along with a Postgres database required for its functioning.
$ docker-compose up -d
Check if the containers are running:
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE ... CREATED STATUS PORTS ...
097f58433a2b hasura/graphql-engine ... 1m ago Up 1m 8080->8080/tcp ...
b0b1aac0508d postgres ... 1m ago Up 1m 5432/tcp ...
Please do note that you will see a Postgres database running, which is used by Hasura to store its configuration (Hasura metadata).
Step 3: Open the Hasura console¶
Head to http://localhost:8080/console to open the Hasura console.
Step 4: Add your MS SQL Server as a source to Hasura¶
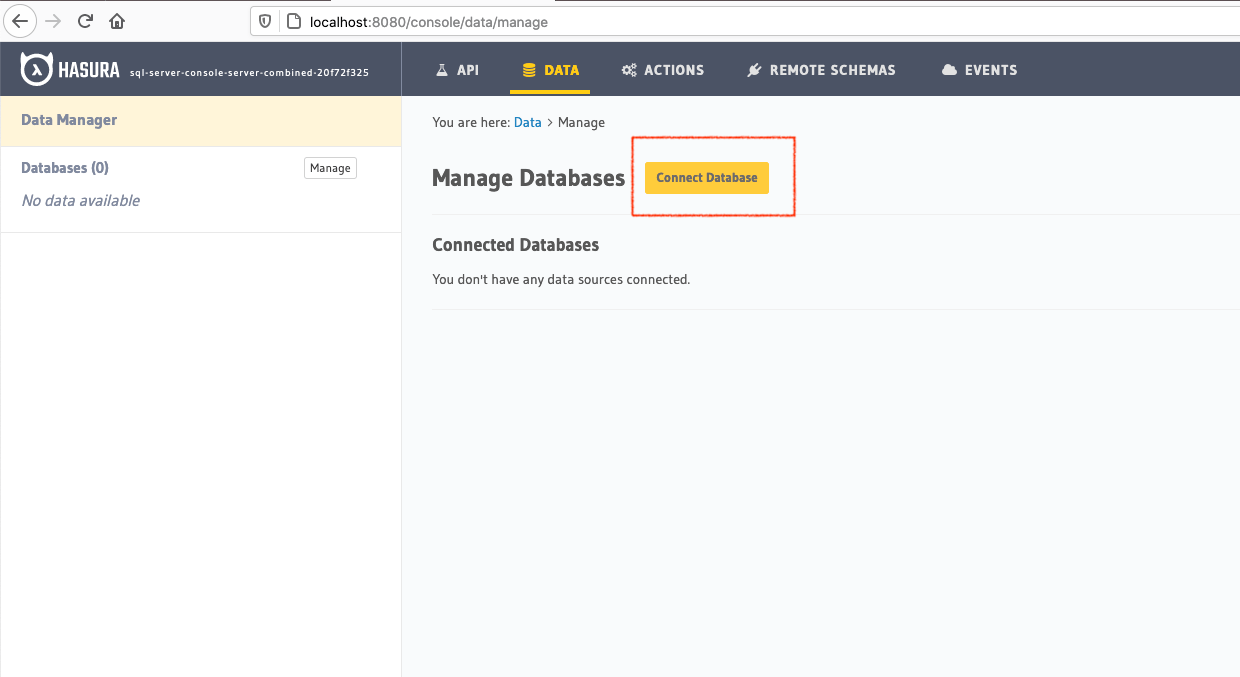
Head to the Data > Manage databases section on the console to add
your MS SQL Server as a source to Hasura. You’ll need your ODBC connection string. Make sure that
your ODBC driver is version 17.
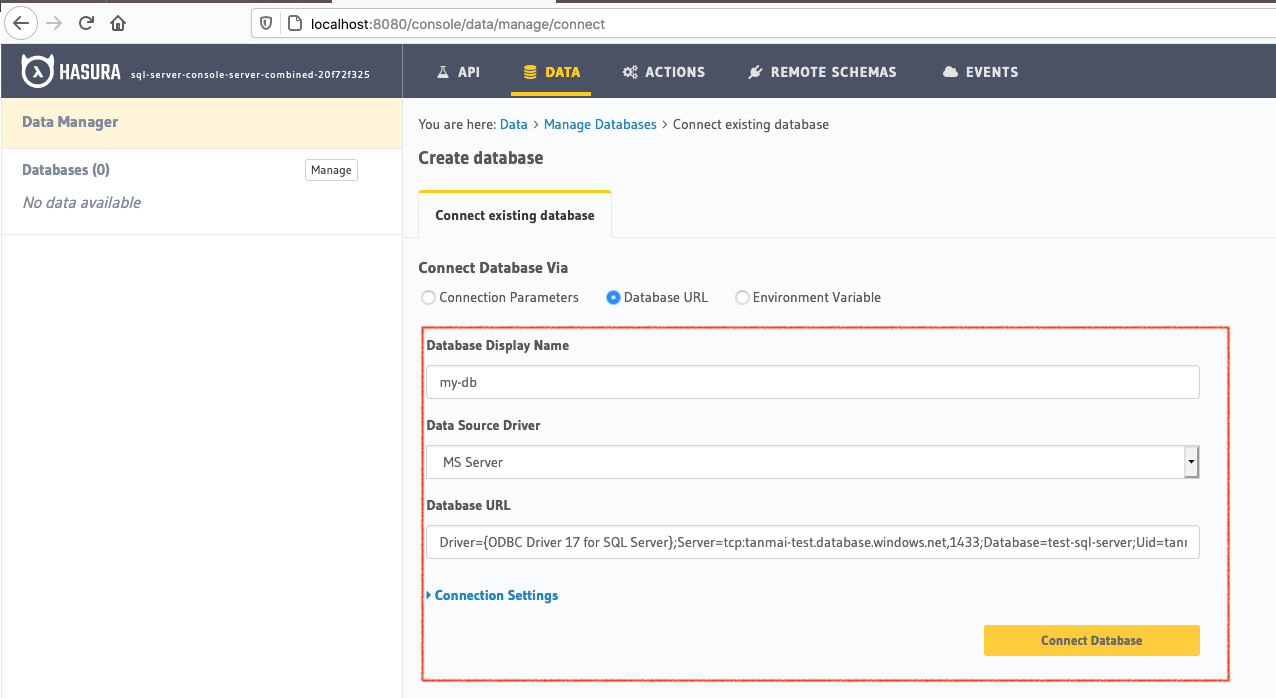
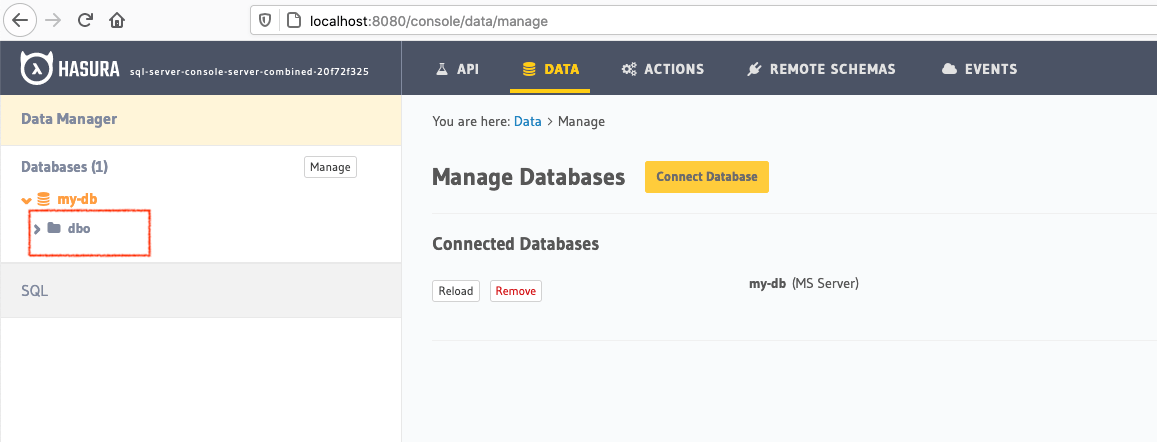
Once you add the database, you’ll see your database pop up on the sidebar.
Step 5: Option 1: Track existing tables¶
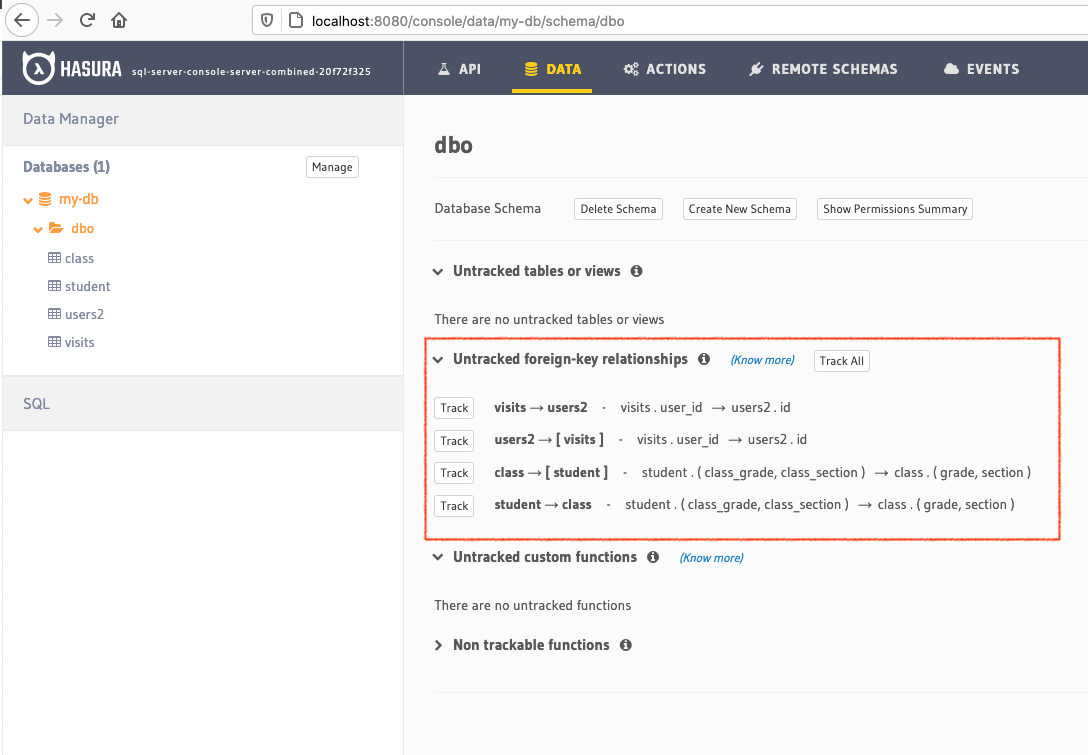
If you have existing tables, head to the database page by clicking on the database name on the sidebar. You should see a list of tables.
Track tables selectively or all of them so that Hasura can introspect the tables and create the corresponding GraphQL schema.
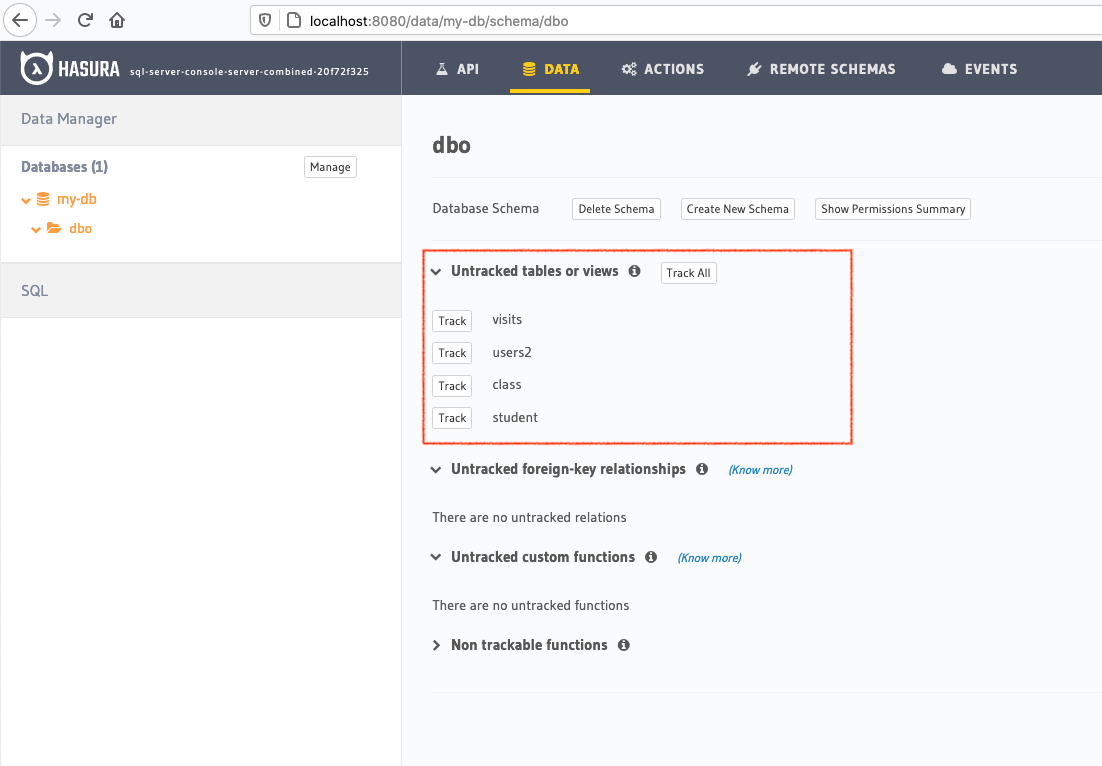
If you have foreign keys, you’ll also see suggested relationships. Again, you can choose to track them selectively or all at once.
Step 5: Option 2: Create new tables¶
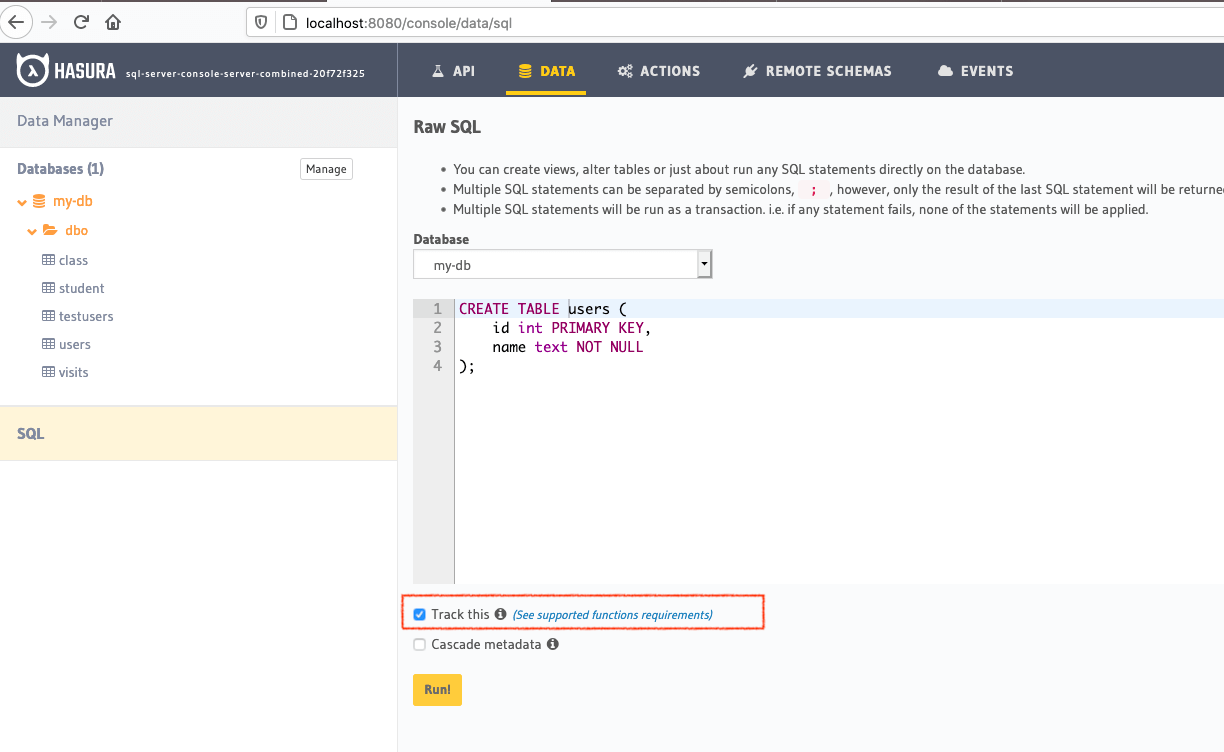
If you don’t have existing tables, head to the Run SQL window to run SQL against your SQL Server database and create tables.
Don’t forget to check “track metadata” at the bottom to make sure Hasura tracks your new database objects in its GraphQL schema.
Step 6: Try out a GraphQL query¶
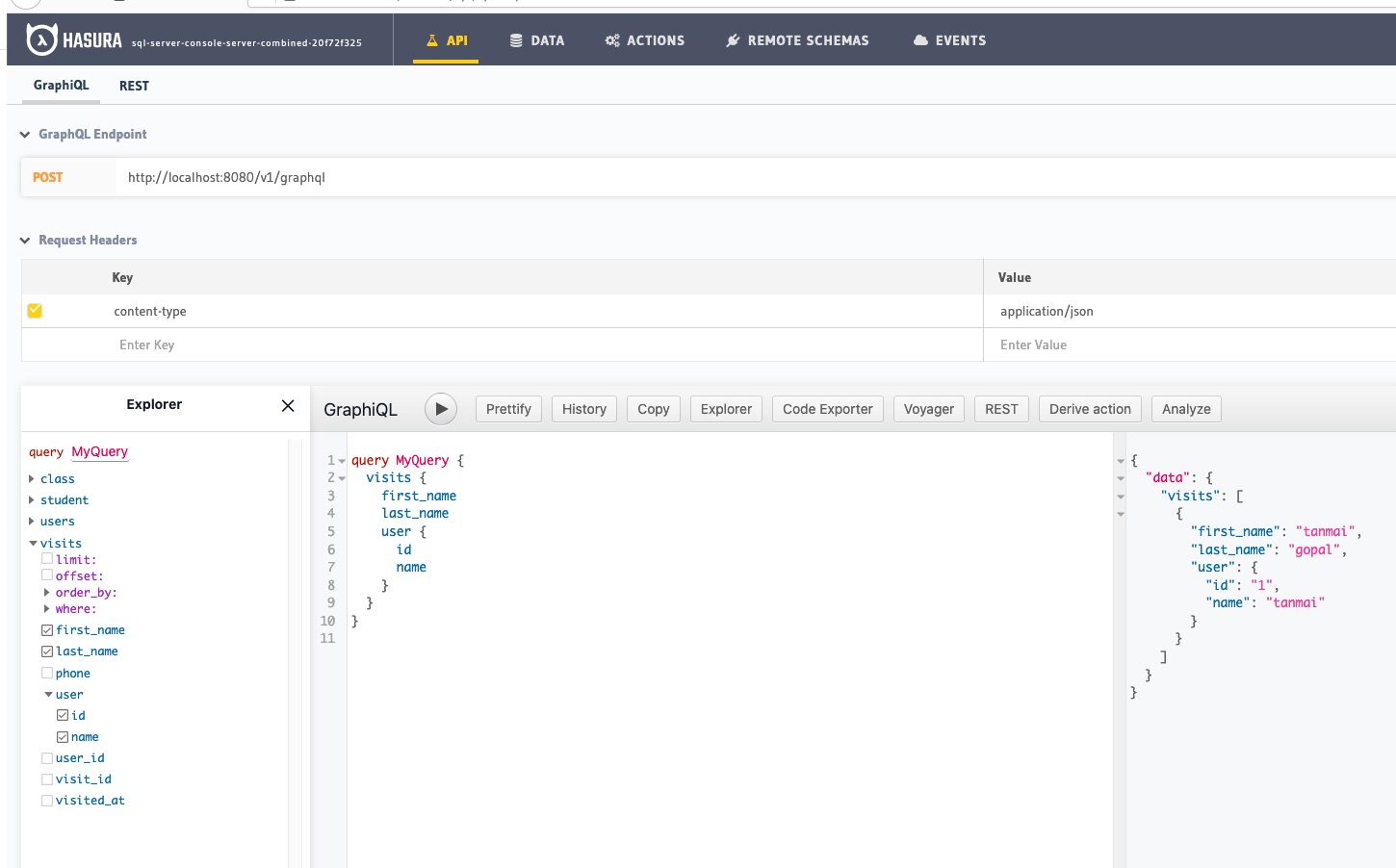
Head to the GraphiQL tab in the console and try running a GraphQL query! Use the explorer sidebar on GraphQL to get help in creating a GraphQL query.
Keep up to date¶
Hasura supports queries, subscriptions, relationships and permissions on MS SQL Server.
Please watch this space to get the latest docs on how you can try these features out via the console or by manipulating metadata in JSON/YAML directly.
If you’d like to stay informed about the status of SQL Server support, subscribe to our newsletter and join our discord!
